

| RQP74037 | |
| I. Background | |
| HVEM (CD270, TNFRSF14) is a human cell surface receptor in the TNF-receptor superfamily that can act as both a co-stimulatory receptor and a co-inhibitory receptor expressed on the surface of T cells. Binding of HVEM to one of its ligands, LIGHT (CD258, TNFSF14) or LTα (lymphotoxin-α), causes a co-stimulatory signal which can activate lymphoid cells. Interaction with BTLA (CD272) or CD160 causes a co-inhibitory signal which negatively regulates T-cell immune responses. HVEM has also been shown to interact with adaptor proteins TRAF2 and TRAF5, and is critical to herpes simplex virus (HSV) cellular entry. | |
| II. Description | |
Recombinant CHO stably expressing human HVEM (TNF receptor superfamily member 14; TNFRSF14; TR2; ATAR; HVEA; HVEM; CD270; LIGHTR; GenBank Accession #NM_003820). | |
| III. Introduction | |
| Host Cell: | CHO |
| Expressed gene: | HVEM |
| Stability: | 32 passages (in-house test, that not means the cell line will be instable beyond the passages we tested.) |
| Synonym(s): | HVEM, TNFRSF14, CD270, HVEA, TR2, LIGHTR |
| Freeze Medium: | 90% FBS+10% DMSO |
| Culture Medium: | F12k+10%FBS+400ug/ml zeocine |
| Application(s): | Binding Assay,FACS |
| Storage: | Liquid nitrogen |
| IV. Description of Host Cell Line | |
| Organism: | Cricetulus griseus, hamster, Chinese |
| Tissue: | Ovary |
| Disease: | Hamster Chinese ovary |
| Morphology: | Epitheloid cell |
| Growth Properties: | Adherent |
| Ⅴ. Representative Data | |
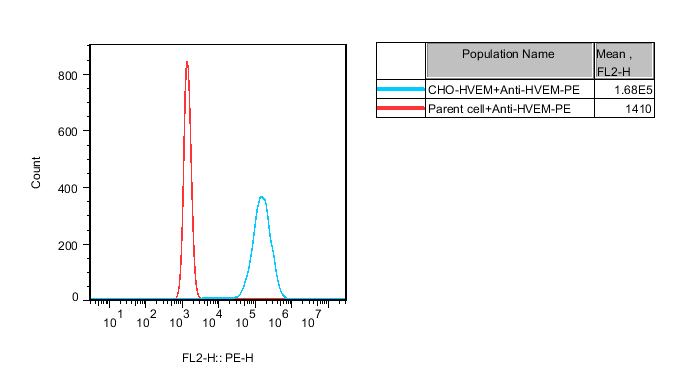  | |
Figure 1. Recombinant CHO stably expressing human HVEM (TNF receptor superfamily member 14; TNFRSF14; TR2; ATAR; HVEA; HVEM; CD270; LIGHTR; GenBank Accession #NM_003820). | |