Cellular Screening Model for PIM-1 Kinase Inhibitors
Background
Moloney murine leukemia virus provirus integration kinase (provirus integration in Maloney murine leukemia virus, PIM) is a highly active serine/threonine kinase, including three subfamily members with high homology (PIM-1, PIM-2, PIM-3). They have obvious differences in tissue distribution: PIM-1 is highly expressed in various leukemia cells and prostate cancer cells; PIM-2 is commonly found in brain cells and lymphocytes; PIM-3 is mainly distributed in kidney and breast. Among them, PIM-1 plays a very important role in regulating cell apoptosis, differentiation, proliferation and tumor formation, and is considered as a potential tumor therapeutic target.
Introduction to PIM-1 Kinase
PIM-1 kinase can phosphorylate many proteins that play an important role in apoptosis and cell cycle regulation, including c-Myc, BAD, Socs1, Cdc25A, HP1, PAP-1, p21cip1/waf1, PTP-U2S, NFATc1 etc. It can also promote the process of cell cycle G2/M and promote cell proliferation and differentiation. PIM-1 can also exert its potential transcriptional repression of STAT5 by acting in combination with Socs1 and Socs3 repressors. PIM-1 can bind to NFATc1 transcription factor and phosphorylate its serine fragment, promote the production of IL-2, and initiate IL-2-dependent proliferation and maturation of lymphocytes.
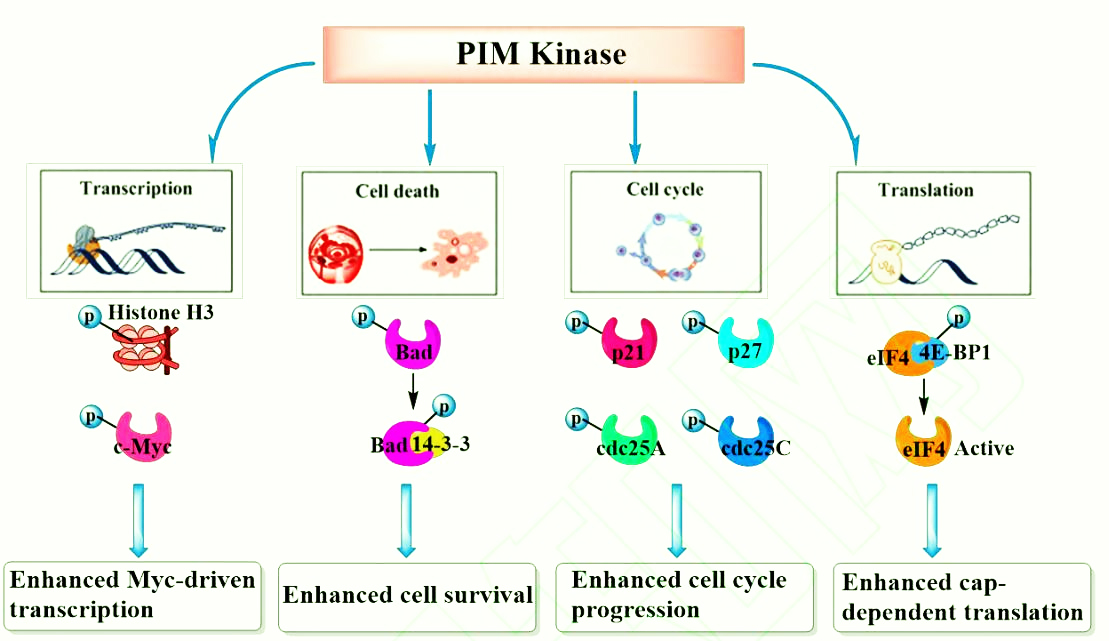
PIM-1 kinase plays a very important role in the proliferation, differentiation and metastasis of tumor cells. Highly expressed PIM-1 kinase causes corresponding biological effects through phosphorylation of different downstream substrate proteins, including accelerating cell cycle progression, promoting transcription and translation, and inhibiting cell apoptosis.
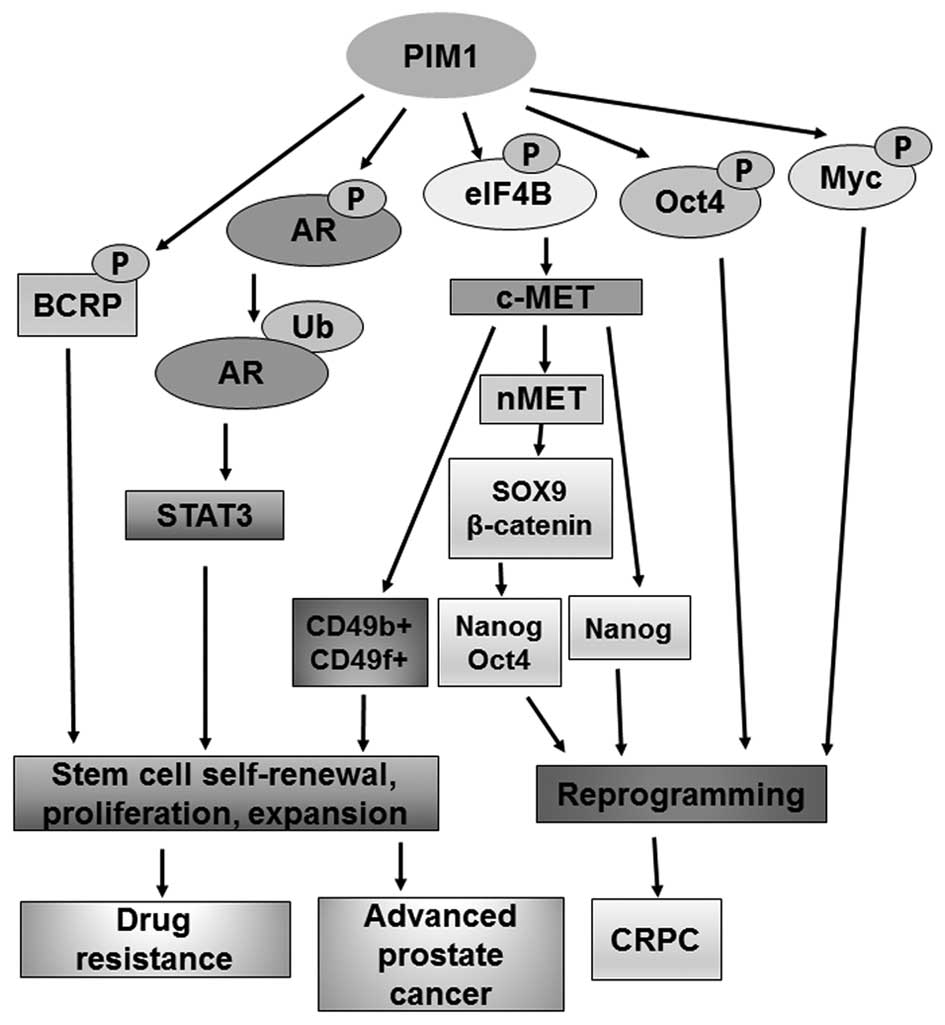
(1) PIM-1 kinase and c-Myc can synergistically promote the occurrence and development of prostate cancer, and the transcriptional activity of c-Myc is significantly enhanced after being phosphorylated by PIM-1.
(2) The pro-apoptotic protein Bad can induce tumor cell apoptosis. After Bad protein is phosphorylated by PIM-1, it will form an inactive stable conjugate, and further activate Bcl-2 protein to play an anti-apoptotic effect.
(3) PIM-1 kinase regulates cell cycle progression by phosphorylating cell cycle inhibitors p21, p27 and phospholipase Cdc25A/C. p21 and p27 have the function of inhibiting the activity of cyclin-dependent kinase CDK, and can prevent the replication of damaged DNA. Phosphorylation of PIM-1 kinase will make it inactive, unable to effectively control the transition of tumor cells from G1 phase to S phase.
(4) PIM-1 kinase can also activate MDR1, BCRP and ABCG2 through phosphorylation, making tumor cells resistant to drugs.
Development Status of PIM-1 Kinase Inhibitors
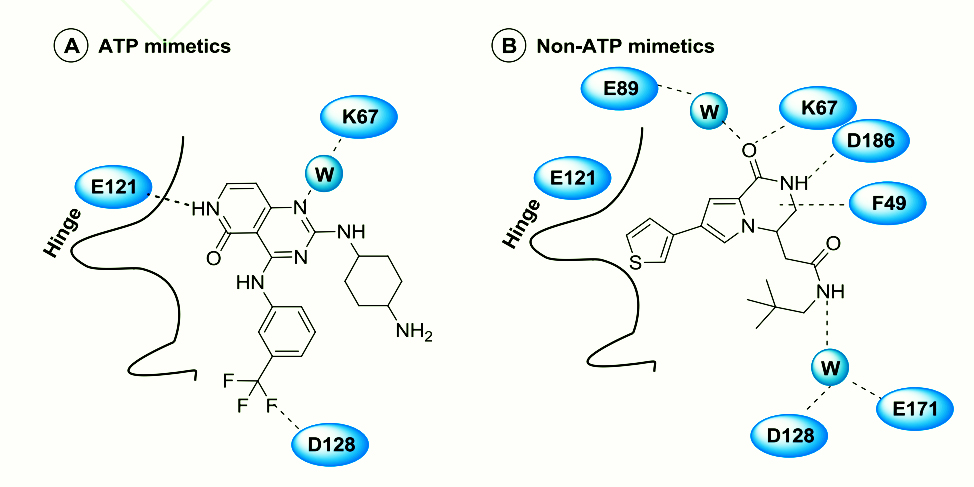
As a serine/threonine kinase with a unique structure, PIM-1 kinase has attracted great attention from major drug research and development institutions. PIM-1 kinase inhibitors of different structural types, including indolecarbazoles, imidazopyridazines, pyridones, etc. According to their binding mode in the PIM-1 protein, they can be divided into two categories: (1) ATP mimics that can directly bind to the E121 residue in the hinge region; (2) non-ATP mimics that bind to the ATP active pocket away from the hinge region They are all ATP competitive inhibitors. At present, most drugs are in the first clinical phase or preclinical research stage, and no drugs have been marketed yet.
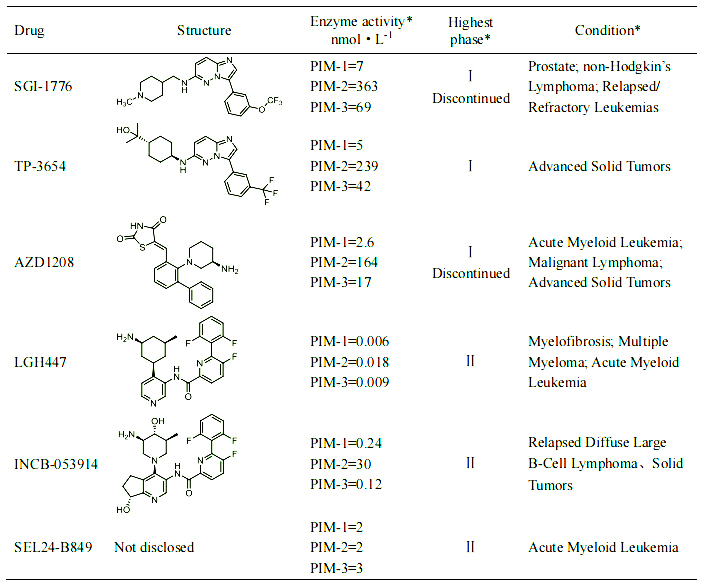
Cell model for drug screening of PIM-1 kinase inhibitors
In response to the needs of PIM-1 kinase inhibitory target mechanism research and new drug development, we has launched a PIM-1 kinase inhibitor drug screening cell model. Some data are shown below. Welcome to inquire.
PIM-1/BaF3l RQP73375
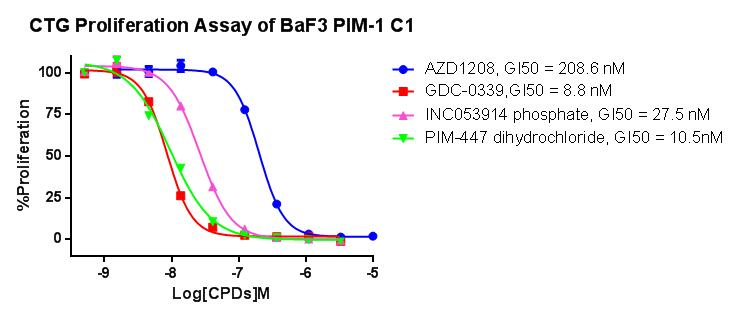
Figure 1. CTG Proliferation Assay of BaF3 PIM-1 C1.

