PD-1/L1 & 4-1BB dual-target cell screening model
In recent years, cancer treatment has achieved a revolutionary breakthrough through immunotherapy that regulates T cell function through immune checkpoint inhibitors represented by the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway. However, a significant proportion of cancer patients do not respond to immune checkpoint inhibitors, and many patients who initially respond will eventually become resistant to immune checkpoint inhibitors due to various mechanisms. The need for novel immune checkpoint therapeutic strategies with broad efficacy. Although immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy can theoretically enhance T cell responses, the resulting antitumor effects do not always occur or are sufficient, whereas targeting costimulatory receptors such as 4-1BB, GITR, and OX- 40 et al) appear to be a promising therapeutic strategy to overcome the unresponsiveness of existing immunotherapies and further enhance the function of exhausted tumor-specific T cells, thereby eliciting a significant antitumor response.
R & D status
Currently, some co-stimulatory receptor-targeting drugs developed based on the above strategies are in the clinical research stage, among which receptor 4-1BB (CD137 or TNFRSF9) is a target that has gained widespread attention. 4-1BB agonist antibodies show potent antitumor effects in various preclinical models as well as in human CD8+ tumor infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs). Urelumab was the first developed 4-1BB agonist antibody, which can induce potent activation of 4-1BB-mediated signaling, but its clinical development was once stalled due to two cases of severe liver toxicity that resulted in the death of patients. This hepatotoxicity may be caused by the activation of 4-1BB signaling on hepatic medullary cells and the subsequent production of interleukin 27. Further studies have shown that Urelumab dose is the most critical factor affecting the development of hepatotoxicity. However, to avoid hepatic It is also questionable whether relatively low doses of urelumab can elicit an adequate antitumor response due to toxicity. Utolimumab is another 4-1BB agonist antibody that has entered the clinic. Although it exhibited mild liver toxicity, it showed poor efficacy in phase I clinical trials. Therefore, the development of 4-1BB agonistic antibodies with minimal hepatotoxicity and sufficient anti-tumor efficacy has become an urgent need for the development of drugs for this target.
In the development of effective immune checkpoint therapy (including immune checkpoint inhibitors, agonistic antibodies and combination therapy, etc.), some new technologies are continuously applied to antibody optimization, in which bispecific antibodies (BsAb) are designed by designing two antigens The strategy of physically linking binding sites to simultaneously act on two different targets has been widely used. Considering that co-stimulatory receptors and ligand complexes must be structurally clustered to deliver a strong co-stimulatory signal, bis-antibodies can be used to induce superclustering of targets such as co-stimulatory receptors while avoiding FcγR-mediated and limit off-target effects by designing the cross-linking of two different molecules, one of which targets a specific location or cell type, thus, compared with combination therapy, double-antibody technology is more effective in targeting co-stimulatory targets. In the development of agonist antibodies, it has unique advantages in terms of specificity and efficacy.
Since 4-1BB is prominently expressed on highly depleted PD-1-high CD8+ TILs and further upregulated after PD-1 blockade, 4-1BB signaling induces clonal expansion of CD8+ TILs, CD8+ TILs exhibit tumor responsiveness without terminal differentiation, so 4-1BB and PD-L1 may be a good pair of mechanisms for inducing T cell antitumor responses. The development of bispecific antibodies against these two is a promising development strategy, which has attracted the participation of domestic and foreign players. At present, more than ten bispecific antibodies against PD-L1/4-1BB are in different R&D stages.
For the research and development of PD-1/L1&4-1BB antibody drugs, especially bispecific antibody drugs, we have specially developed a PD-1/L1&4-1BB dual-target cell screening model, which can measure the activity and evaluate PD- 1/L1&4-1BB combined drug and the efficacy of bispecific antibody, product information and related data are as follows:
PD1/41BB Dual Effector Reporter Cell RQP74172
PD-L1 aAPC Cell RQP74164
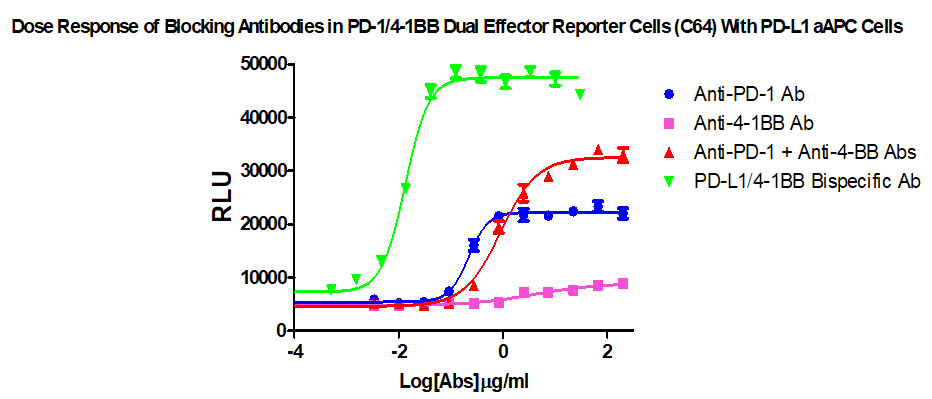
Figure 1. Dose Response of Blocking Antibodies in PD-1/41BB Dual Effector Reporter Cells (C64) With PD-L1 aAPC Cells.

