New product release【Thalassemia standard product】
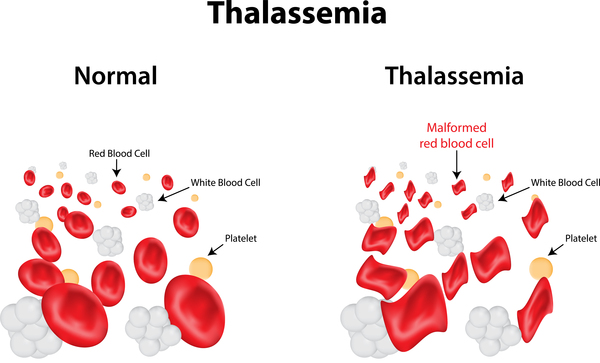
Thalassemia is referred to as "thalassemia" in English. Thalassemia was first discovered by two scientists, Thomas Cooley and Pearl Lee, in the Mediterranean region in 1925. But in fact, the disease is widely distributed in tropical and subtropical regions. In China, the southern provinces generally have a higher incidence rate, such as Guangdong, Guangxi, Hainan, Yunnan, etc. About 20% of the people carry the thalassemia gene, and the incidence rate is about 10%.
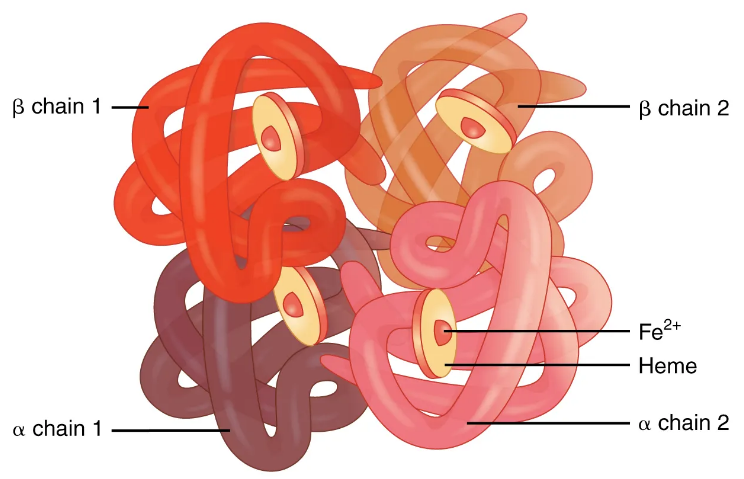
Hemoglobin is the protein responsible for carrying oxygen in human red blood cells. Hemoglobin consists of four subunits, two alpha subunits and two beta subunits. In an electrolyte solution similar to the human environment, the four subunits of hemoglobin can automatically Assembled into α2β2 morphology. Each subunit of hemoglobin is composed of a peptide chain and a heme molecule. The peptide chain will be coiled and folded into a spherical shape under physiological conditions, and the heme molecule will be held in it. The spherical structure formed by the coiled peptide chain is also called. globin. The heme molecule is a small molecule with a porphyrin structure. In the center of the porphyrin molecule, the nitrogen atoms on the four pyrrole rings in the porphyrin are coordinated and combined with a ferrous ion. The nitrogen atom on the indole side chain of the histidine residue is coordinated to the ferrous ion from above the plane of the porphyrin molecule. When hemoglobin is not bound to oxygen, there is a water molecule from below the porphyrin ring. The iron ions bind in coordination, and when the hemoglobin carries oxygen, the oxygen molecules replace the water.
Introduction to Thalassemia
Thalassemia can be divided into two categories according to the different pathogenic gene variants: α-thalassemia and β-thalassemia. Alpha-thalassemia refers to thalassemia caused by pathogenic mutations in the alpha-globin gene. Similarly, β-thalassemia is thalassemia caused by pathogenic mutations in the β-globin gene.
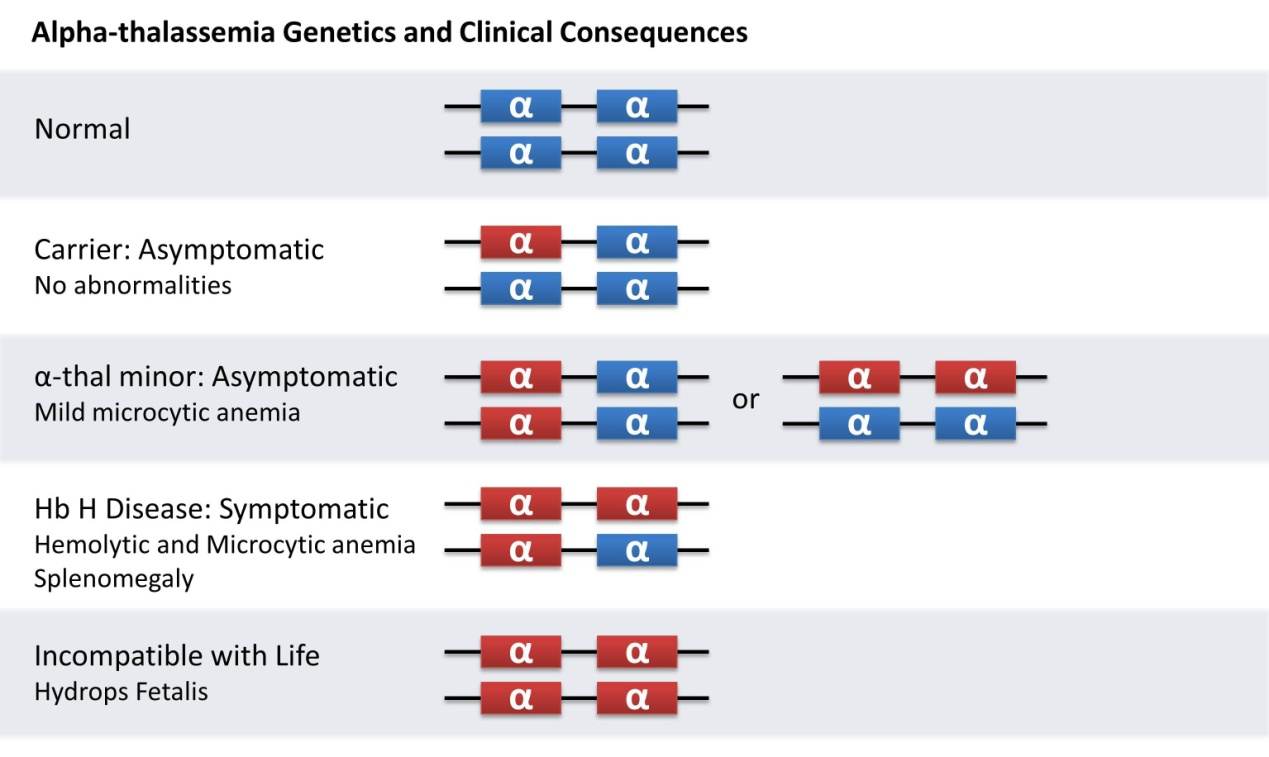
The alpha globin gene is located on chromosome 16. A normal human chromosome has two copies of the alpha globin gene arranged in tandem. Two chromosomes have four copies of the alpha globin gene. Pathogenic variants in alpha globin may result in thalassemia, which manifests primarily as a loss of copies of alpha globin, which can be 1, 2, 3, or even 4 deletions, in Asian and African Americans Most common. Among them, the most common α-globin deletions in Chinese are:--SEA, -α3.7 and -α4.2.
Decreased α-globin synthesis results in a relative excess of β-globin chain production and a reduction in the overall production of hemoglobin. Decreased total hemoglobin production produces typical thalassemia microcytic anemia. However, a relative excess of β-globin production results in a hemoglobin tetramer consisting entirely of β-globin tetramers, termed Hb H. Although Hb H is somewhat soluble, it is more easily oxidized and has a higher affinity for oxygen than normal Hb A. Not only does this lead to inefficient delivery of oxygen to tissues, but oxidized HbH tends to accumulate in red blood cells, leading to extravascular hemolytic anemia, which can lead to splenomegaly. Hb H also appears to be ineffective in inducing some degree of erythropoiesis.
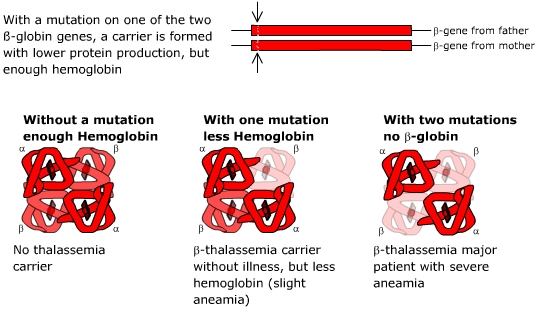
The gene of β-globin is located on chromosome 11, and each chromosome 11 of normal people contains 1 copy of β-globin. In total, normal people have 2 copies of β-globin gene. β-globin gene mutation is mainly caused by abnormal coding, unable to synthesize β-globin, or the synthesized β-globin cannot be combined with α-globin, thus unable to form normal and functional hemoglobin. β-thalassemia is generally caused by mutations in β-globin. Common mutations in Chinese are: CD41-42, IVS-2-654, CD17, -28, CD26, CD71-72, CD43, -29, Int, CD14 -15, CD27-28, -32, -30, IVS-1-1, IVS-1-5, CD31 and Cap.
Beta-thalassemia minor (usually heterozygous)
Patients with beta-thalassemia minor are usually asymptomatic and present with a very mild hypochromic microcytic anemia that may be discovered incidentally. Sometimes, symptoms associated with mild anemia may occur.
Beta-thalassemia major (usually homozygous)
Patients with β-thalassemia major may present with severe hypochromic microcytic anemia and become transfusion dependent due to chronic ineffective erythropoiesis and extravascular hemolysis. Compensatory hyperplasia of the erythropoietic component in the bone marrow can lead to bone deformities. Extramedullary hematopoiesis and splenic hemolysis often lead to hepatosplenomegaly.
地贫检测现状
The detection of thalassemia has a long history. Since 2015, more than 10 companies have obtained registration certificates, and one company has registered multiple certificates. The most important method is the PCR method, and there are also some chip methods and enzymes. Combined immunoassay, colloidal gold method, etc. In 2022, BGI will obtain the registration certificate for NGS detection of thalassemia.
Based on market demand, we have also developed molecular diagnostic standards for α-thalassemia and β-thalassemia, some of which have completed internal verification and will be put on the shelves soon.
Partial product data
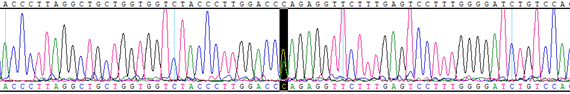
HBB GLN39TER (CAG>TAG)
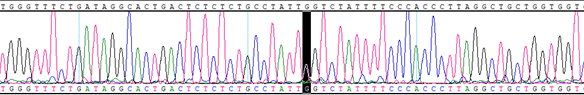
HBB IVS1, G>A, +110 Heterozygous
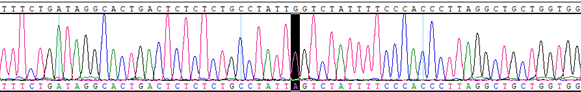
HBB IVS1, G>A, +110 Homozygous

HBB -87C>G Heterozygous
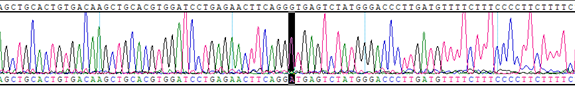
HBB IVS2, G>A, +1 Homozygous
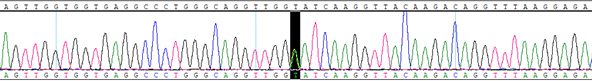
HBB IVS1, T>C, +6 Heterozygous
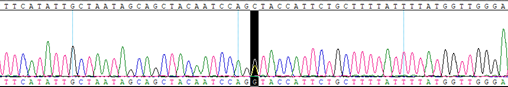
HBB IVS2, C>G, +745 Heterozygous

