【Product Promotion】IL23 Antibody Screening Model
Introduction to IL23 and its receptor
Interleukin-23 (IL-23) was first reported in 2000 when a new sequence (p19) was discovered that combined with the p40 subunit of IL-12 to produce a new active cytokine complex Things. It is secreted by activated dendritic cells, and compared with IL-12, its biological characteristics are both common and different.
IL-23 is a member of the IL-12 cytokine family, which also includes members such as IL-12, IL-27, IL-35 and IL-39, which are a unique set of heterodimeric cytokines, It is usually composed of an α chain subunit (p19, p28, or p35) and a β chain subunit (p40 or Epstein-Barr virus-induced gene 3), and signals are transduced through the JAK/STAT pathway. IL-23 binds to the heterodimeric receptor complex composed of IL-23R and p40 subunits through its p19 subunit and transmits signals. Similarly, IL-12 uses its p35 and p40 subunits, respectively. It binds to the IL-12Rβ2 and IL-12β1 subunits of the IL12 receptor to transduce signals.
IL-23 receptor is mainly expressed on natural killer cells, macrophages, memory T cells (Th17) and keratinocytes, and as a response to microbial pathogens or wound healing signals, IL-23 is produced by It is secreted by activated dendritic cells and macrophages and is recruited with neutrophils.
Physiological and pathological effects of IL23 and its signaling pathway
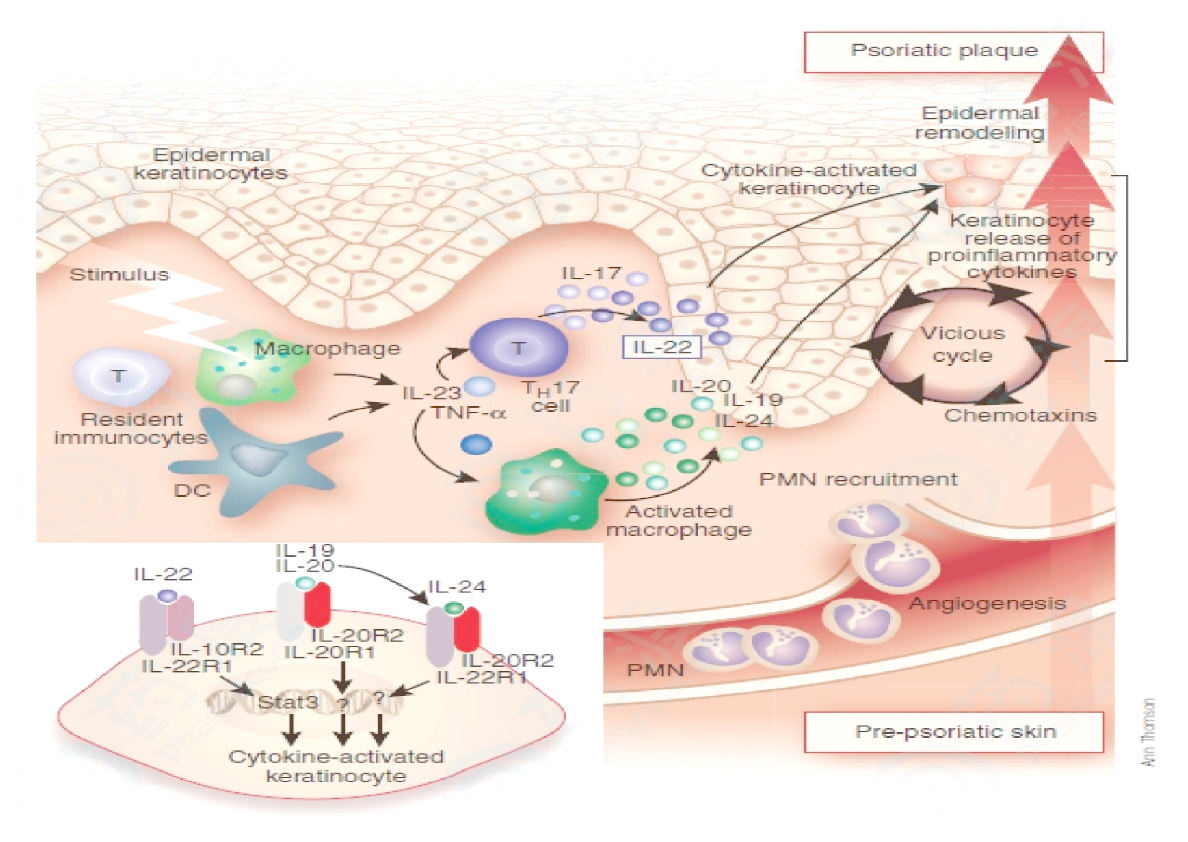
IL-23 mainly acts on Th17 cells. When IL-23 binds to Th17 cells, it initiates signal transmission by recruiting tyrosine kinases TYK2 and JAK2 to IL-12Rβ1 and IL-23R, respectively, and then these kinases will be further phosphorylated It also activates the downstream transcription factor STAT3, and also activates other members of the STAT family to a lower degree, including STAT4, STAT1, and STAT5. The phosphorylated STAT3 complex transfers to the nucleus and induces the expression of IL-17A, IL-23R and the transcription factor retinoic acid-related orphan receptor-γt, thus playing an important role in the proliferation and stabilization of Th17 cells. However, when IL23 is over-activated, it will also promote Th17 cells to produce a large amount of IL-17A, IL-22 and other cytokines. These factors act on keratinocytes and cause keratinocyte activation and excessive proliferation. The activated keratinocytes will further produce a large number of cytokines, chemokines and antimicrobial peptides, etc., recruit and activate immune cells such as T cells, forming a cascade of immune responses, and triggering the occurrence of psoriasis. (The picture below shows the mechanism of IL-23/IL-17 pathway involved in the pathogenesis of psoriasis)
Development of IL23 antibody drugs
According to the mechanism of IL23 involved in the pathogenesis of psoriasis, a neutralizing antibody against IL23 was developed for the treatment of psoriasis. Ustekinumab developed by Johnson & Johnson is a fully humanized IL-12/IL-23 IgG1 monoclonal antibody It is also the first antibody drug to act on the IL-23/IL-17 signaling pathway. It binds to the p40 subunit of IL-12/IL-23, thereby reducing the production of Th17 and Th1 and its downstream IL-17 , IL-6, TNF-α and other cytokines, so as to achieve the purpose of treating psoriasis. The drug was approved for the treatment of psoriasis in 2009, was approved for psoriatic arthritis in 2013, and was subsequently approved for the treatment of Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis and other diseases. Indications Continuous expansion has brought rich returns for manufacturers.
Recent studies have shown that the secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-17, IL-22 and IL-21 by Th17 induced by IL23 is the main factor in psoriasis inflammation and plaque formation. The selective targeting of IL-23p19 subunits may preserve the disease response ability of IL-12 Th1 and have potential therapeutic advantages. Recently, some anti-IL-23p19 antibody drugs including Guselkumab, Tildrakizumab, and Risankizumab have been approved for moderate to severe plaque psoriasis, as well as Crohn’s disease, hidradenitis suppurativa, psoriatic arthritis, and ulcers. Clinical trials are also being carried out for multiple indications of autoimmune diseases such as colitis, atopic dermatitis, ankylosing spondylitis, asthma, etc., which shows good application prospects. In addition, there are many similar products at home and abroad in follow-up research and development.
IL23 cell screening model
For the development of IL23 antibody drugs, we have developed related cell screening models, which can be used for functional cell-level screening and live measurement.
Part of the product data
IL23 Effector Reporter Cell RQP74130
Figure 2. Dose Response of Recombinant Human IL23 in Human IL23 Effector Reporter Cells (C6).
Figure 3. Inhibition of lL23-induced Reporter Actity by IL 23 Neutralizing Antibody in IL23 Effector Reporter Cells (Clone6).

