[Target model + diagnostic quality control] Drug development and diagnosis of BCR-ABL1
Chronicmyelogenus (CML) is also known as chronic myeloid leukemia, chronic myeloid leukemia or chronic granulocyte leukemia) is a bone marrow proliferative tumor that is generated as mature and unsuccessful granulocytosis. Controlled proliferation, cell differentiation is normal.
CML and 2 genes were integrated with 2 genes: BCR (at 22 "chromosome) gene and ABL1 (located on chromosome) gene forming a BCR-ABL1 fusion gene. This abnormal fusion is usually due to the phase 9 chromosomes and 22 chromosomes, that is, T (9; 22) (Q11), producing an abnormal 22 chromosome, called Philadelphia (pH) chromosome, this Derived 22 chromosome contained Bcr-ABL1 fusion gene.
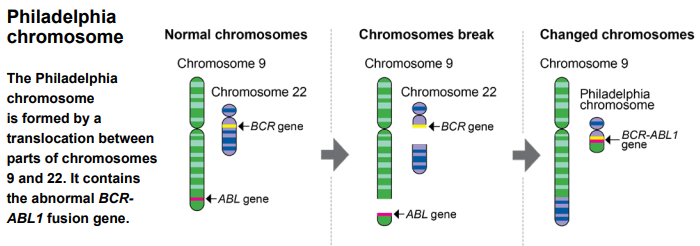
Figure 1. Ectopic chromosome formation BCR-ABL1 fusion
The BCR-ABL1 fusion gene can produce a unique gene product, i.e., BCR-ABL1 fusion protein. The protein product comprises an enzymatic domain from normal ABL1, has a tyrosine kinase catalytic activity; the kinase activity relative to normal ABL1 is strictly regulated, since the BCR portion is fused, and the kinase activity of BCR-ABL1 has increased and has a constitutive type. Expressed, this lost controlled tyrosine kinase participated in the pathogenesis of CML.
The BCR-ABL1 fusion gene is more common in more than 95% of CML. Different according to the fracture site of the BCR gene, it can be divided into major fracture point clustering regions (mass, m-bcr, e13a2 or e14a2, encoded P210), secondary fracture point The cluster region (Minor, M-BCR, E1A2, encoded P190), mini breakpoint cluster region (MICRO, μ-BCR, E19A2, encoded P230). Most CML express P210; very small number expression P230, the chemotherapy is low; about 2/3 of PH + ALL expression P190.
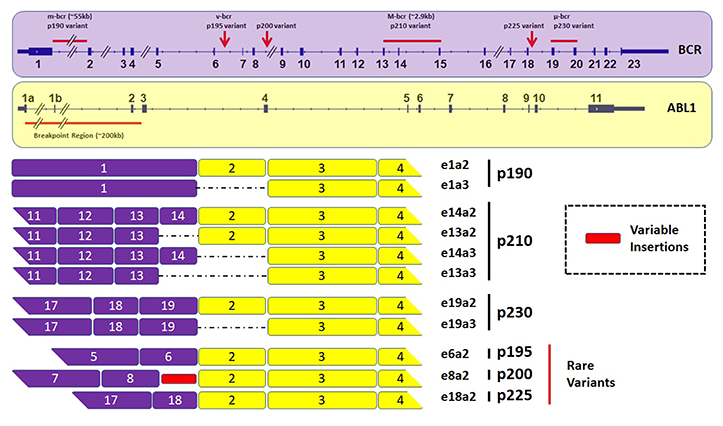
Figure 2. Typing of BCR-ABL1 fusion
Signal path of BCR-ABL1
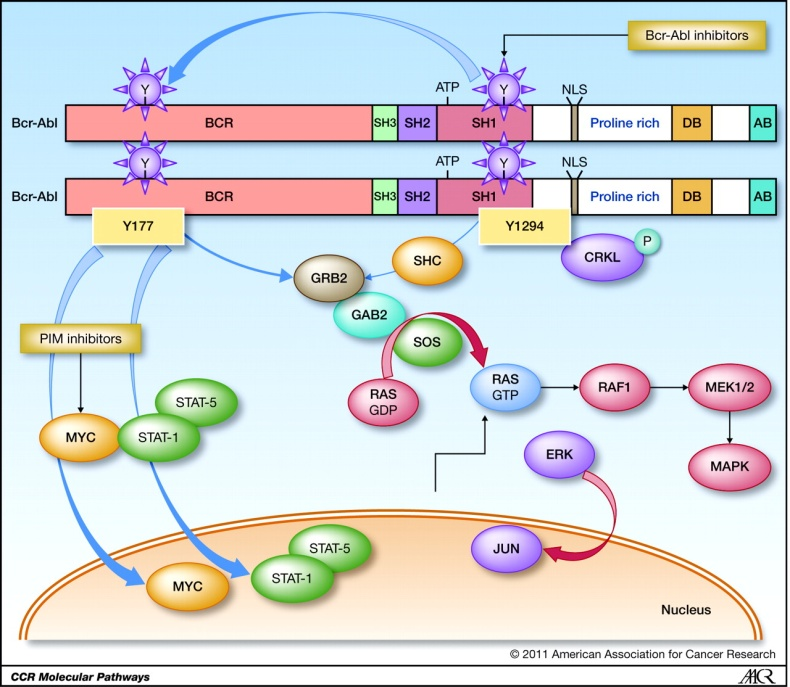
Figure 3. Schematic diagram of the molecular pathway activated by Bcr-abl
BCR TYR177 BCR-ABL phosphorylation is essential for BCR-ABL-mediated leukemia. BCR-ABL / GRB2 complex recruits SOS, which is related to the composition of GRB2SH3 domain. BCR-ABL / GRB2 / SOS complex stimulates the non-active GDP binding form to translate into its active GTP binding state, and activate the bracket joint Gab2. Thus, the GRB2 / Gab2 / SOS complex causes the formation of the RAS downstream path to activate the MEK1 / 2 and MAPK proteins and cause abnormal cell proliferation.
In addition, BCR-ABL via Pi3k / Akt / FoxO4 and ultimately the up-regulation of MTOR effectively blocks important cells, such as autophagy.
Another assumption of BCR-ABL protein conversion activity is a raw carcinoma gene Myc, which is expressed in CML cells. Myc activation seems to be independent of the RAS path, but directly by the ABLSH2 region.
Although the BCR-ABL activated path list seems to have endless expansion, and the complexity revealed in these paths is increasing, all conversion functions of BCR-ABL do seem to depend on their tyrosine kinase activity. This prerequisite has an incredible intrinsic clinical potential in developing more complex targeted treatments.
Diagnosis of BCR-ABL1
In the NCCN Guide and Expert Consensus, the recommended diagnostic methods are generally divided into three kinds of FISH, Q-PCR, SEQUENCING, and FISH can find the ectopicity of BCR-ABL1, and the same can also be made analysis, found 9 Number and 22nd changes. The Q-PCR focused on the change of the expression of BCR-ABL1 in mRNA levels, which can be qualitatively or quantitative. The development of sequencing technology can help BCR-ABL1 detection, whether it is a generation sequencing or second-generation sequencing, can be found from the cDNA level, or the change of the purpose gene can also be found in the GDNA level.
Standard
As a company specializing in providing molecular diagnostic standards, we offer a variety of products (GDNA, RNA, CTDNA, FFPE, etc.) about BCR-ABL1, involving a variety of technical platforms, quality control management of the entire process, is also suitable Development and verification of LDT and IVD.
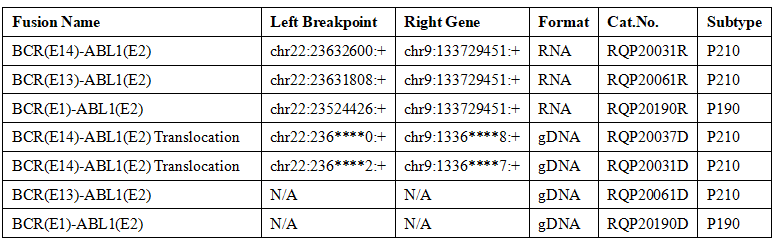
Table 1. Molecular diagnosis standards of common BCR-ABL1
Some data display
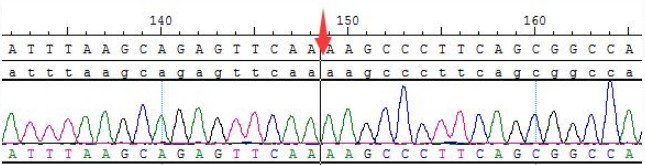
Figure 4. Sanger sequencing of bcr (e14) -abl1 (e2) for RNA
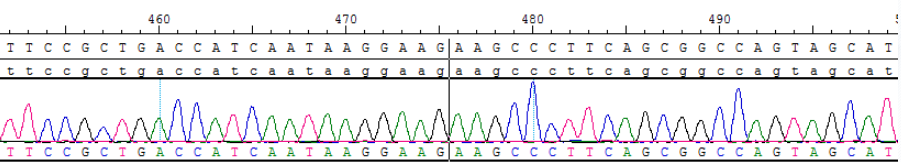
Figure 5. Sanger sequencing of BCR(E13)-ABL1(E2) for RNA
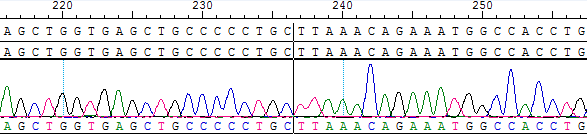
Figure 6. Sanger sequencing of BCR(E14)-ABL1(E2) Translocation for gDNA
BCR-ABL1 drug development
Imatib is the first list of BCR-ABL1 TKI, selectively inhibits C-ABL1, C-Kit and PDGFRα / β tyrosine kinase activity, but after the first-line treatment, BCR-ABL1 dependence Sex and undepended resistance.
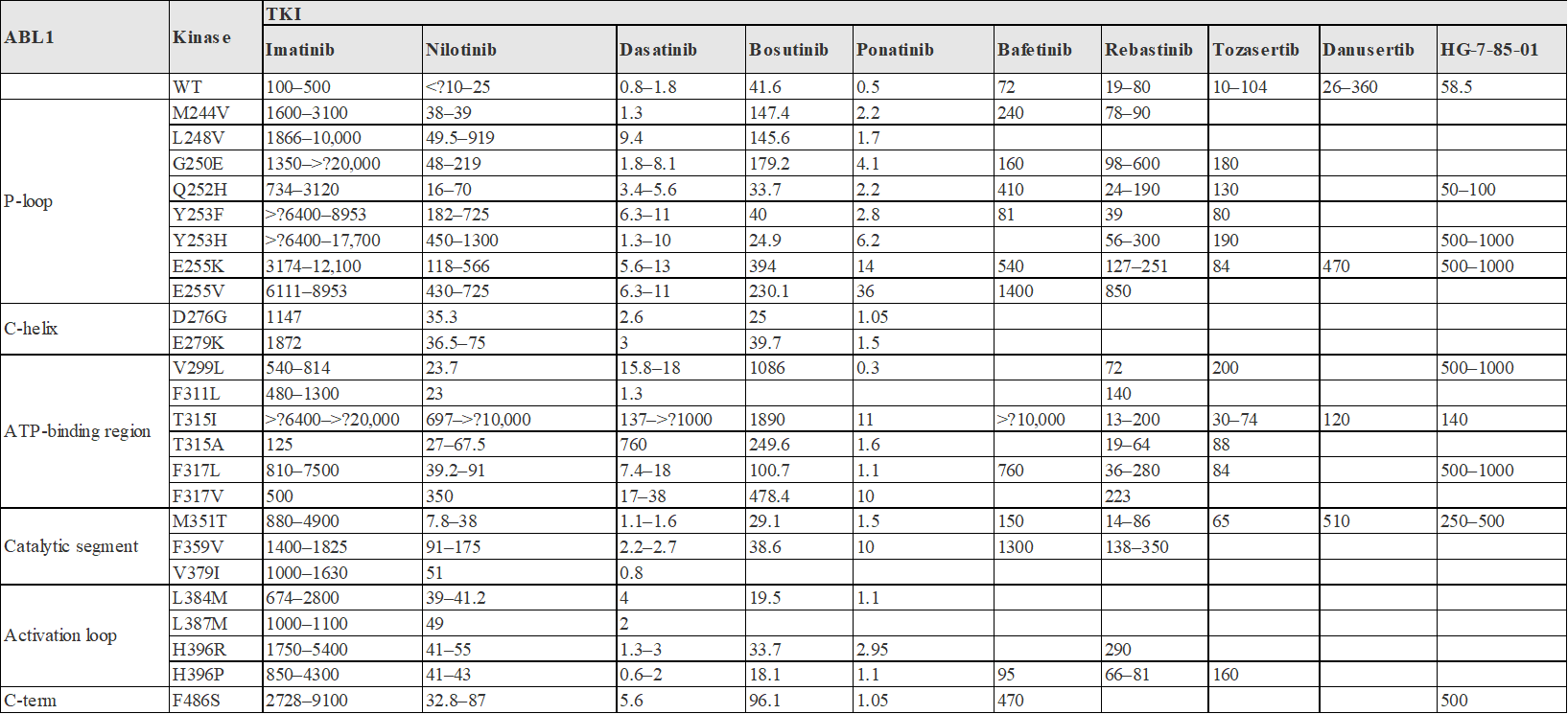
Figure 7. IC50 (NM) of the TKI of BCR-ABL in Cell-Based Assay to WT and Different Drug-resistant IC50 (NM)
Drug target model
For BCR-ABL1 and its common drug-resistant sites, Kobe creatures have developed a variety of Cell-Based Kinase Assay models, which can be used for the activity detection of TKI's in Vitro and In Vivo, suitable for early compound survival screening, also Fit product release QC.
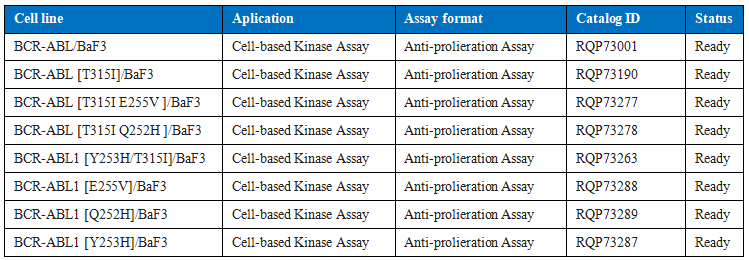
Table 2. Drug R & D models of some common BCR-ABL1
Other more sites (such as M244V, G250E, D276G, P465S, V468F, I502L, P223S, K294E, E355G, etc.) are being developed.
Some data display
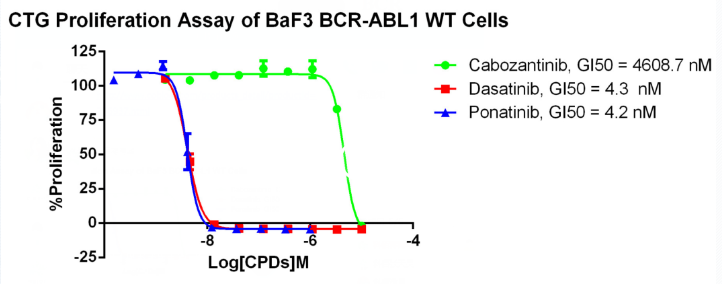
Figure 8. Anti-proliferation assay of three reference compounds on the BCR-ABL1/BaF3 Stable Cell Line.
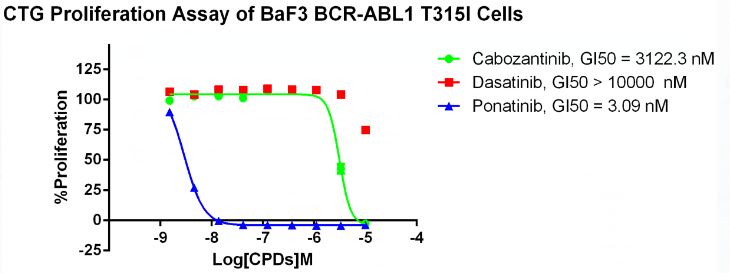
Figure 9. Anti-proliferation assay of three reference compounds on the BCR-ABL1[T315I]/BaF3 Stable Cell Line.
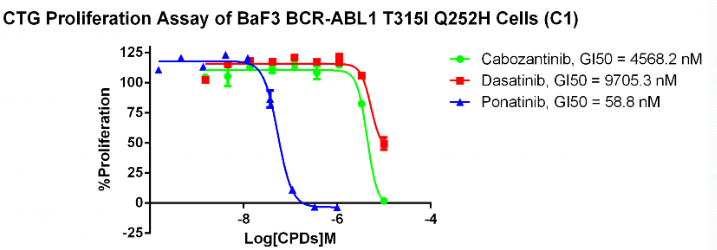
Figure 9. Anti-proliferation assay of three reference compounds on the BCR-ABL1[T315I]/BaF3 Stable Cell Line.

