IL36 Target Drug Cell Screening Model Drug
Background
IL-36 and IL36R pathways play a very important role in the body's inflammatory response, are important factors in inflammatory diseases, and belong to the IL-1 family. The IL-36 subfamily consists of three similar agonistic ligands IL-36α, IL-36β, IL-36γ and IL-36 receptor antagonist (IL-36Ra). IL-36 mediates intracellular signal transduction through IL-36 receptor (IL-36R) and IL-1 receptor accessory protein (IL-1RAcP). Studies have shown that the mutation and inactivation of the gene encoding IL-36Ra can cause IL-36R signal dysregulation, mainly manifested as diffuse pustular psoriasis, indicating that IL-36 plays an important role in the skin inflammation of psoriasis. Further studies have shown that IL-36 also plays an important role in inflammatory diseases of other organs. The development of IL-36 and IL36R drugs has become an important direction for the treatment of inflammatory diseases.
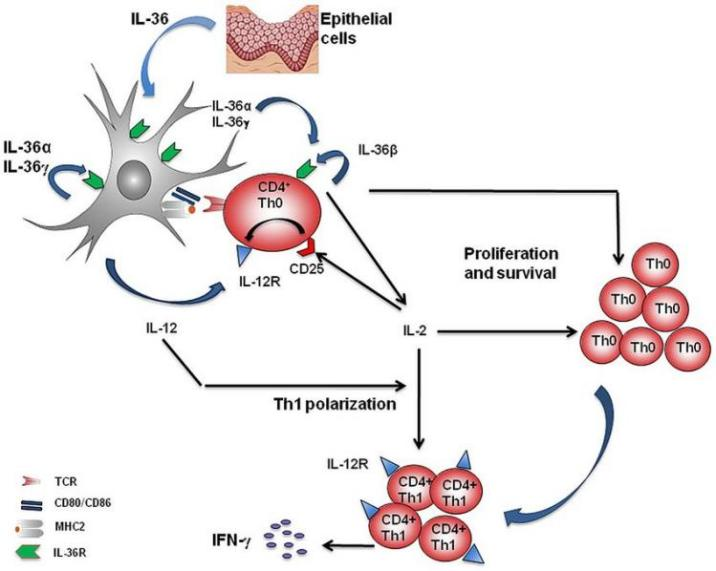
IL-36α, IL-36β, and IL-36γ combine with IL-36R in the body to activate the MAPK/NF-kB pathway to promote inflammation and participate in the activation, maturation, polarization, and antigen extraction of dendritic cells and T cells. Present and stimulate the production of pro-inflammatory factors and other functions. IL-36Ra is an IL-36R receptor antagonist and can also be combined with IL-36R to inhibit and regulate IL-36R activity.
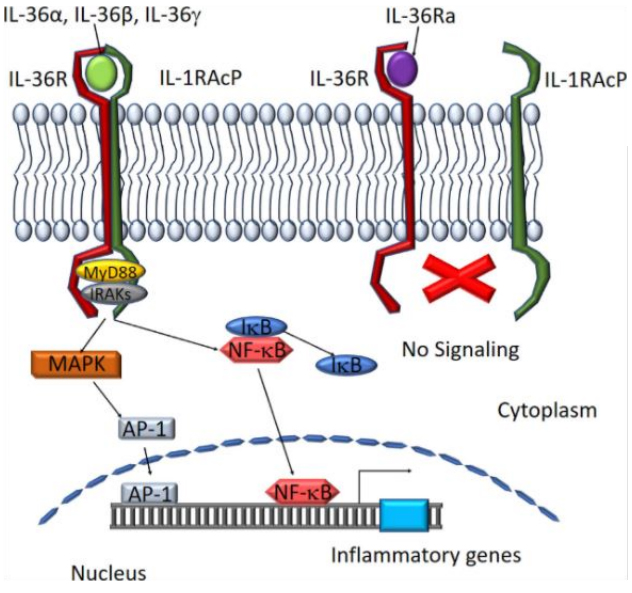
In vivo, if IL-36RA is mutated and inactivated, IL-36 signaling cannot be inhibited. IL36R continues to be abnormally activated, induces the expression of chemokines and cytokines, and promotes various inflammatory cells such as macrophages and neutrophils. The infiltration and activation of granulocytes and Th17 cells, as well as the release of cytokines such as IL-17, TNF and IL22, can further up-regulate the expression of IL36 in skin cells and dendritic cells, and further amplify the inflammatory response. Eventually, a large number of neutrophils and other immune cells are recruited on the surface of the skin to form patches of pustules, leading to General pustular psoriasis (GPP).
Current status of IL-36 target drug development
Drugs targeting IL36 targets can act either by binding to IL-36R receptors, or by binding to IL-36α, IL-36β, and IL-36γ. Drugs that are currently in the clinical stage mainly work by targeting its receptor IL-36R, including antibody drugs such as imsidolimab and Spesolimab. The analysis of the existing clinical progress data shows that the IL-36R antibody has an ideal therapeutic effect and safety for pustular psoriasis GPP, but has a mediocre effect on palm and plantar psoriasis. Studies on the indications of IL36 target drugs for other inflammatory diseases such as ulcerative colitis, Crohn’s disease, atopic dermatitis, ichthyosis, hidradenitis suppurativa and acne are still ongoing.
(1) Boehringer Ingelheim developed the IL-36R blocking antibody Spesolimab (BI 655130), and was one of the first companies to use monoclonal antibodies that block IL-36 receptors in the field of skin diseases. Boehringer Ingelheim is currently developing the drug for the treatment of a variety of immune disease indications. Skin diseases include Generalized Pustular Psoriasis (GPP), Palmoplantar Pustulosis, PPP), Hidradenitis Suppurativa (HS) and atopic dermatitis (AD), among which pustular psoriasis, which is the most suitable disease, is currently in phase II clinical stage.
(2) AnaptysBio has developed another antibody, Imsidolimab (ANB019), which inhibits the function of IL-36R. It is planned to be used for pustular psoriasis, palmoplantar pustulosis, EGFR-mediated dermatotoxic ichthyosis, and purulent Hidradenitis and acne, etc. Phase II clinical trials of pustular psoriasis and palmoplantar pustulosis have been completed, and the phase 2 clinical trials of moderate to severe palmoplantar pustulosis did not reach the primary endpoint. Imsidolimab was granted orphan drug designation by the FDA due to its excellent efficacy in phase II clinical trials of pustular psoriasis. Phase 3 clinical trials are expected to start in mid-2021.
IL36 target drug cell screening model
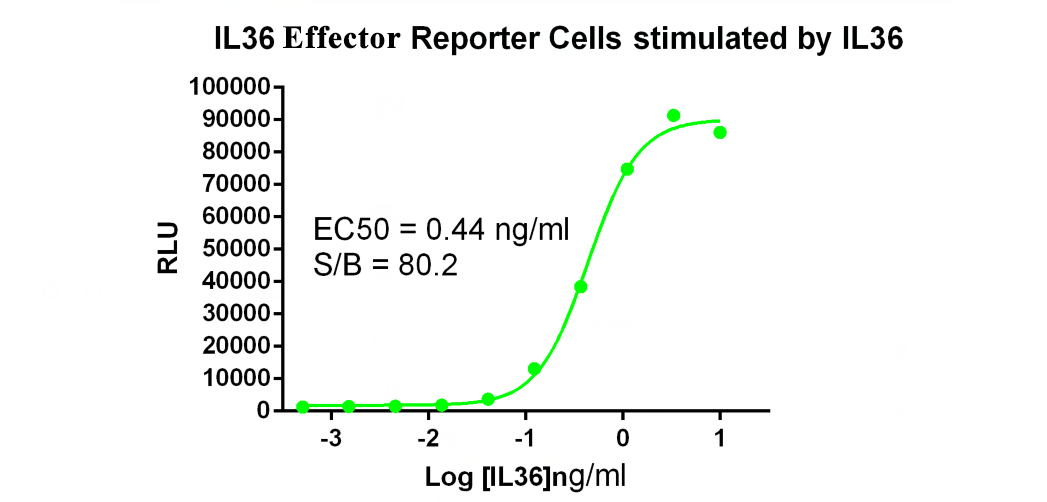
In response to the needs of IL-36 and IL36R pathway target drug development and target research, Kebai Biosciences has developed the IL36 Effector Reporter Cell drug screening cell line. Welcome to inquire.
IL36 Effector Reporter Cell RQP74119